
How to Assembly an Electromagnetic Clutch
Proper mounting of an electromagnetic clutch is crucial to ensure efficient operation of industrial and agricultural machinery. In this comprehensive guide, we explain step-by-step how to perform a professional installation, the available mounting types, and the most important technical considerations.
What is an Electromagnetic Clutch?
An electromagnetic clutch is a device that uses the electromagnet principle to couple and decouple two rotating shafts. It works through a stationary coil that generates a magnetic field, attracting a mobile armature when direct current is applied, thus creating the mechanical connection between the two parts.
Main components:
- Electromagnetic coil: Generates the magnetic field.
- Coil holder or inductor: Concentrates the magnetic force lines.
- Armature or induced element: Element that is attracted when energising the coil.
- Friction material: Provides adherence and durability.
- Rotor: Rotating contact surface.
Types of Electromagnetic Clutches and Their Mountings
1. Clutches with Slip Rings
Characteristics:
Coil holder connected to a hub with slip rings; electrical supply through fixed brushes
Mounting:
Fix the hub with slip rings to the driving shaft. Install the brush holder in a stationary position and verify correct brush pressure.
2. Clutches with Stationary Coil and Rotor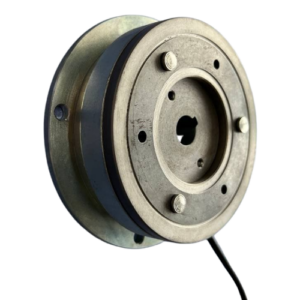
Characteristics:
Fixed coil mounted on the machine; rotating rotor as friction surface. Offers a longer service life and less maintenance.
Mounting:
Fix the coil holder to a static part of the machine. Align the rotor perfectly with the driving shaft, verifying concentricity and perpendicularity.
Step-by-Step Mounting Process
Preliminary Preparation
- Technical specification verification
- Required torque vs nominal clutch torque
- Maximum rotation speed
- Supply voltage (generally 24V DC)
- Mounting dimensions
- Required tools
- Allen keys and fixed wrenches according to specifications
- Calibrated torque wrench
- Multimeter for electrical verifications
- Calliper, micrometre or feeler gauges for precision measurements
Mechanical Mounting
Step 1: Coil Holder Installation
Position the coil holder and ensure it is fixed to a completely static part of the machine to prevent vibration.
Step 2: Rotor Alignment
Mount the rotor to the driving shaft with the corresponding key. Use a dial indicator to verify concentricity.
Step 3: Armature Installation
Place the armature on the driven shaft. Adjust the position to obtain the correct air gap (typically 0.2 – 0.5 mm). Ensure the air gap is uniform across the entire circumference.
Electrical Connection
Basic Supply Circuit
- Typical supply requires a transformer (from 220V AC to 24V DC) and a rectifier.
- Recommended Connections: Connect the positive and negative terminals to the coil.
- Protections: It is highly recommended to install a protection diode, varistor, or Zener diode in parallel to protect the contacts from overvoltage during disconnection.
Recommended Connections
- Direct current side
- Connect positive to one coil terminal
- Negative to the other terminal
- Install a protection diode in parallel (optional)
- Protection elements
- Varistor or Zener diode to protect contacts
- Capacitor in parallel to smooth disconnection
Important Technical Considerations
- Rotation Speed: Never exceed the tabulated limits (e.g., Type SEE ranges from 1,400 to 10,000 RPM depending on size).
- Break-in Process: New clutches may initially show reduced torque (up to 50%). They require several hundred actuations to reach full nominal torque.
- Maintenance: Regularly inspect the air gap and check friction surfaces for grease or oil contamination, which significantly reduces torque.
Troubleshooting Common Problems
| Problem | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Insufficient Torque | Excessive air gap or oil on surfaces | Adjust air gap / Clean with degreaser |
| Excessive Noise | Mechanical misalignment | Verify concentricity and perpendicularity |
| No Engagement | Faulty electrical supply | Check voltage (24V DC) and coil continuity |


